Introdution
利用labelme制作coco格式的实例分割数据集,该数据集适用于mmdetection2.0中的mask部分。
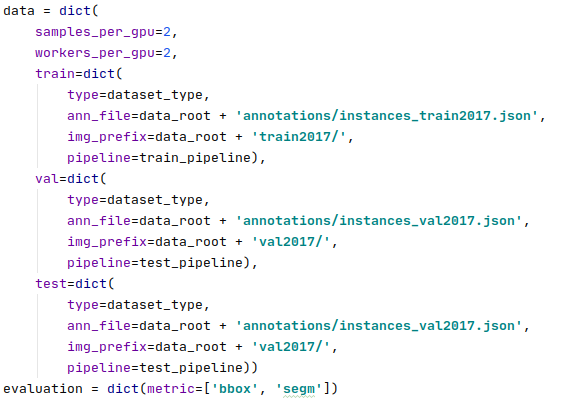
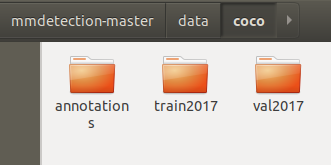
在mmdetection2.0框架下,利用coco格式的数据集进行实例分割默认只需要train2017和val2017两部分(当然也可以将test中的目录修改成test2017,但没必要)。
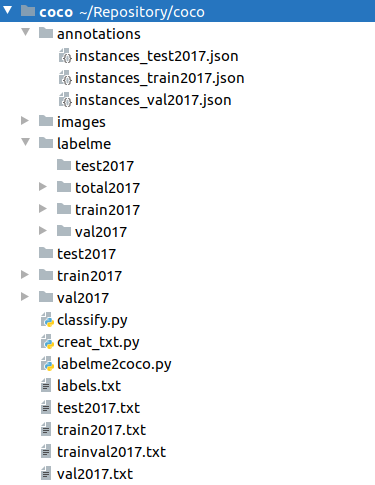
mmdetection2.0框架下coco格式数据集文件如下图放置:(运行完本文的.py文件后即可生成以下文件夹)
数据集标注方式:
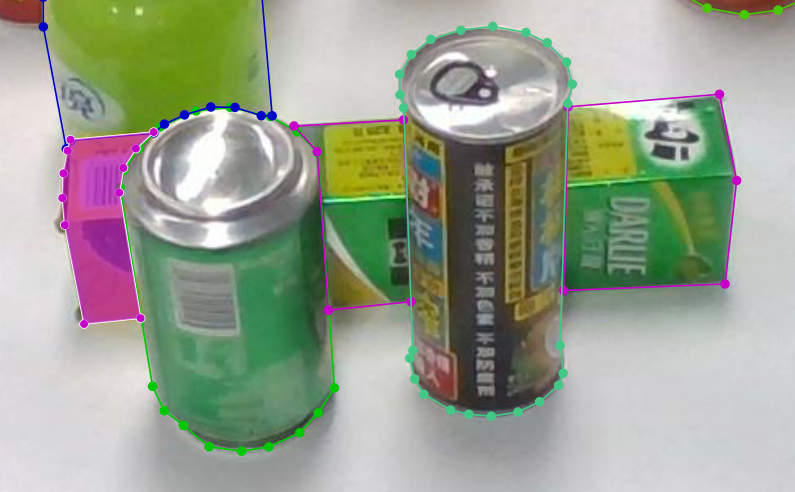
当一张图片里没有多个同类别的物体,使用car,computer,bottle等标签直接进行标注;当一张图片里同个类别有多个物体时,标签采用sofa-1,sofa-2,desk-1,desk-2等标签-数字的格式进行标注;如果同一物体在遮挡情况下被分为多个部分,则不同部分都用同一个标签(具体如下图所示,牙膏的三个部分标签均为toothpaste)。
最后得到的json文件里的segmentation是分为三部分,bbox只存在一个(在笔者找的其他资料里,都是分为三个独立的牙膏部分,得到三个segmentation以及三个相应的bbox,显然不符合实际情况)。
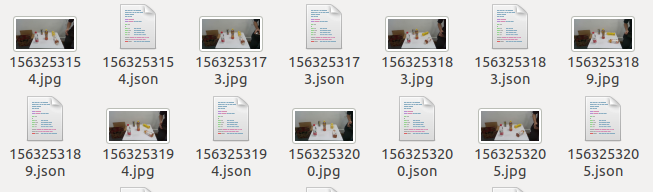
建议在使用labelme进行对数据集标注时,将生成的.json文件放置在与数据集相同的路径下以避免一些不必要的麻烦。即下图:
否则,生成的json文件里的imagePath可能出现下图所示的情况:
如果实在是没办法,没有在同一路径下,imagePath会比较复杂(可能是windows系统用\分隔号,ubuntu系统则会是/分隔号,这一点是笔者的猜测),根据不同的情况修改后文代码。
Solution
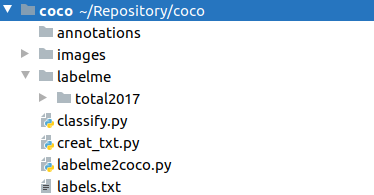
各文件夹布局如下所示:
所有的.jpg文件放在images文件夹下,所有的.json文件(labelme标注完成后生成的文件)放在labelme/total2017文件夹下。
creat_txt.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
# !/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import random
trainval_percent = 1 # No test sample
train_percent = 0.9
jsonfilepath = 'labelme/total2017'
txtsavepath = './'
total_xml = os.listdir(jsonfilepath)
num = len(total_xml)
list = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
ftrainval = open('./trainval2017.txt', 'w')
ftrain = open('./train2017.txt', 'w')
fval = open('./val2017.txt', 'w')
ftest = open('./test2017.txt', 'w') #Still create test2017.txt
for i in list:
name = total_xml[i][:-5] + '\n'
if i in trainval:
ftrainval.write(name)
if i in train:
ftrain.write(name)
else:
fval.write(name)
else:
ftest.write(name)
ftrainval.close()
ftrain.close()
fval.close()
ftest.close()
print('Create_txt Done')
classify.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
import shutil
import os
import os.path as osp
sets=['train2017', 'val2017', 'test2017']
for image_set in sets:
if osp.exists(image_set):
shutil.rmtree(image_set)
print('Deleted previous %s file and created a new one'%(image_set))
os.makedirs(image_set)
json_path = 'labelme/%s'%(image_set)
if osp.exists(json_path):
shutil.rmtree(json_path)
print('Deleted previous %s file and created a new one' % (json_path))
os.makedirs(json_path)
image_ids = open('./%s.txt'%(image_set)).read().strip().split()
for image_id in image_ids:
img = 'images/%s.jpg' % (image_id)
json = 'labelme/total2017/%s.json'% (image_id)
shutil.copy(img,image_set)
shutil.copy(json,'labelme/%s/'% (image_set))
print("Done")
labelme2coco.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
#!/usr/bin/env python
import collections
import datetime
import glob
import json
import os
import os.path as osp
import sys
import numpy as np
import PIL.Image
import labelme
import shutil
try:
import pycocotools.mask
except ImportError:
print('Please install pycocotools:\n\n pip install pycocotools\n')
sys.exit(1)
def main():
sets = ['train2017','val2017','test2017']
output_dir = './annotations'
if osp.exists(output_dir):
print('Output directory already exists:', output_dir)
shutil.rmtree(output_dir)
os.makedirs(output_dir)
print('Creating dataset:', output_dir)
for set in sets:
input_dir = './labelme/%s'%(set)
filename = 'instances_%s'%(set)
now = datetime.datetime.now()
data = dict(
info=dict(
description=None,
version=None,
contributor=None,
date_created=now.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f'),
),
licenses=[dict(
id=0,
name=None,
)],
images=[
# license, url, file_name, height, width, date_captured, id
],
type='instances',
annotations=[
# segmentation, area, iscrowd, image_id, bbox, category_id, id
],
categories=[
# supercategory, id, name
],
)
class_name_to_id = {}
for i, line in enumerate(open('labels.txt').readlines()):
class_id = i - 1 # starts with -1
class_name = line.strip()
if class_id == -1:
assert class_name == '__ignore__'
continue
class_name_to_id[class_name] = class_id
data['categories'].append(dict(
supercategory=None,
id=class_id,
name=class_name,
))
out_ann_file = osp.join(output_dir, filename+'.json')
label_files = glob.glob(osp.join(input_dir, '*.json'))
for image_id, label_file in enumerate(label_files):
with open(label_file) as f:
label_data = json.load(f)
path=label_data['imagePath'].split("\\") # 可能因为windows或ubuntu不同的系统用\\或/划分,详见前言三
img_file = './%s/'%(set) + path[-1]
img = np.asarray(PIL.Image.open(img_file))
data['images'].append(dict(
license=0,
url=None,
file_name=label_file.split('/')[-1].split('.')[0] + '.jpg',
height=img.shape[0],
width=img.shape[1],
date_captured=None,
id=image_id,
))
masks = {} # for area
segmentations = collections.defaultdict(list) # for segmentation
for shape in label_data['shapes']:
points = shape['points']
label = shape['label']
shape_type = shape.get('shape_type', None)
mask = labelme.utils.shape_to_mask(
img.shape[:2], points, shape_type
)
if label in masks:
masks[label] = masks[label] | mask
else:
masks[label] = mask
points = np.asarray(points).flatten().tolist()
segmentations[label].append(points)
for label, mask in masks.items():
cls_name = label.split('-')[0]
if cls_name not in class_name_to_id:
continue
cls_id = class_name_to_id[cls_name]
mask = np.asfortranarray(mask.astype(np.uint8))
mask = pycocotools.mask.encode(mask)
area = float(pycocotools.mask.area(mask))
bbox = pycocotools.mask.toBbox(mask).flatten().tolist()
data['annotations'].append(dict(
id=len(data['annotations']),
image_id=image_id,
category_id=cls_id,
segmentation=segmentations[label],
area=area,
bbox=bbox,
iscrowd=0,
))
with open(out_ann_file, 'w') as f:
json.dump(data, f,indent=4)
print(set + ' is done')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
上述三个文件按顺序执行即可。
最后所有的文件夹如下图所示,如前文所提到的,在mmdetection中被利用到的只有annotations,train2017,val2017三个文件夹。
本文的代码可以反复运行,因为代码中包含一些旧文件夹的删除以及新建,不会报错。